How to Create Book Club Magic Using Essential Questions {Part One}
Lackluster literature circles? Boring book clubs? The remedy: lose traditional “role” sheets, declare freedom from organization by topic or genre, and build essential question-focused literature circles or book clubs instead. An EQ as the throughline for your lit circle/book club unit kicks up the impact that comes from having kids talk about what they read in a way that just does not happen with any other method. Here’s why:
REASON #1: CHOICE, BUT LIKE, FOR REAL
Fundamental Tenet of Lit Circles and Book Clubs
Fact: choice boosts student engagement. And even in the “passage picker, summarizer, questioner, illustrator” role sheet days of early lit circles, students selected books that most interested them – usually within a specific genre or topic.
Great, right?
Sort of.
What about students who:
detest dystopia?
hate historical fiction?
can’t stand “coming of age”?
They have choice. Among titles they wouldn’t otherwise pick for themselves.😕
When lit circles and book clubs focus on essential questions (more info on essential questions and inquiry-based learning here and here), novel options for students – unbound by any constraints other than shedding light on the question – grow exponentially!
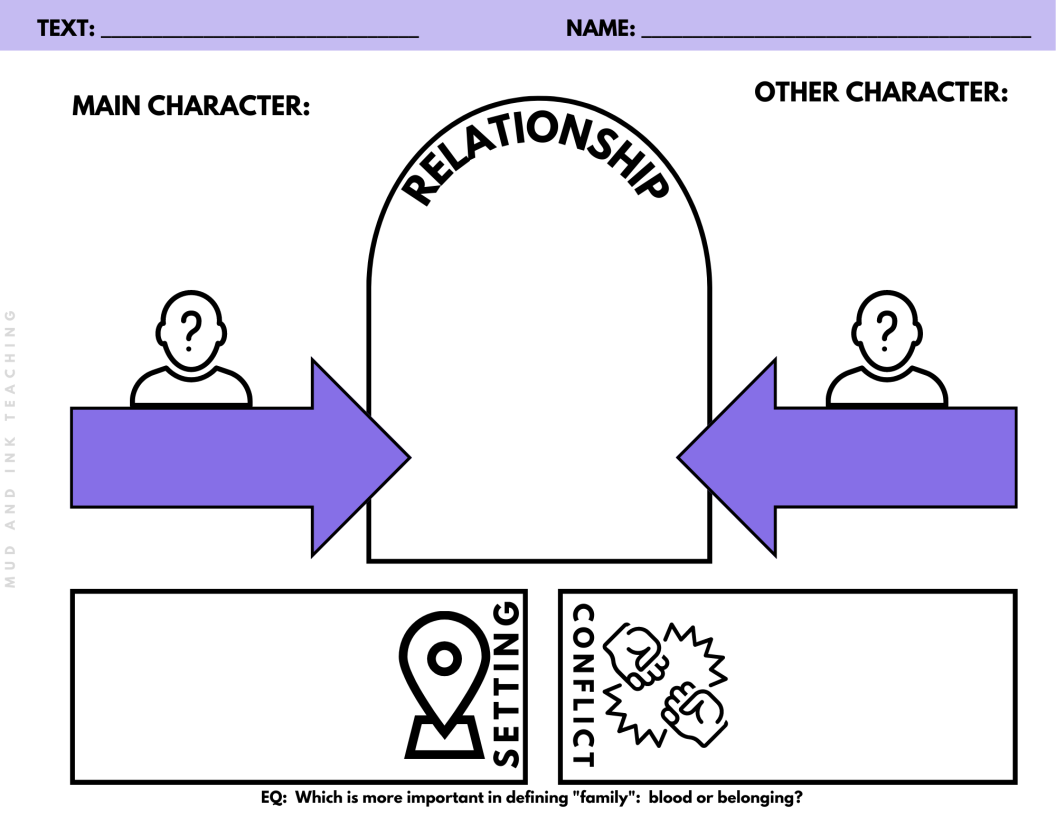
For example, if your book club/lit circle essential question is why do relationships matter? book choices could include:
The Outsiders
The Hunger Games
and The Crossover
or
The House on Mango Street
Long Way Down
and The Children of Blood and Bone.
Classics. Novels in verse. Realistic fiction. Fantasy. Dystopia.
Something for every student's interest and background, and this is just a short list of possibilities for tackling this EQ! The EQ focus makes the book selection more authentic for the kids. Instead of “the least worst option,” their choice becomes something that truly speaks to their personal preferences as readers thereby creating more emotionally engaged lit circle/book club participants who are ready to tackle the EQ!
CHECK OUT AMANDA’S FAVORITE BOOKS TO USE IN A RELATIONSHIPS EQ UNIT:
REASON #2 – RIGOR
EQ-focused lit circles and book clubs elevate rigor!
While choice certainly helps open the door to student engagement, rigor plays a role, too. By rigor, I do NOT mean offering only complex texts, accelerated reading calendars, or piling on assignments.
As high school reading and writing gurus Kelly Gallagher and Penny Kittle say in their latest book, 4 Essential Studies, rigor does not equal text difficulty.
““Book clubs motivate us to read. They deepen our understanding of not only the book but how others read and interpret the same text … rigor is not in the book itself, but in the work the students do to understand it” (45-47). ”
And the work students do with EQ-focused book clubs or lit circles encourages this work.
Sure, in a genre-based book club, the kids can examine what elements show up in their book and how. They can compare how one author achieves this versus another.
But an EQ, like Which is more powerful: hope or fear? immediately asks students to sit with uncertainty and consider possible answers and solutions rather than identify more correct ones.
EQ-based lit circles or book clubs meet students where they are – literal, theoretical or anywhere in between – and provide opportunities to scaffold toward analysis, synthesis and more abstract thinking.
How?
One way is to use supplemental texts and pairings!
These texts are not novel-specific but EQ-connected, so every book group can use them:
articles
poems
songs/lyrics
art pieces
videos
stories
book excerpts
Supplementals and pairings can be used to create whole-class, lit circle-based, or jigsawed skill-focused lessons that students can then practice independently. Check out my EQ Adventure Packs for supplementals and pairings AND a choice board that can also be used for this purpose.
What might such a lesson look like?
Your EQ: what is more powerful: hope or fear?
Skill focus: writing analytical paragraphs (students hyperfocus on literal aspects of plot)
Whole group: listen to one of the songs, give kids a copy of the lyrics
Whole group: model identifying where you notice hope or fear in the lyrics; think-aloud noting which felt stronger and why
Small groups: kids continue identifying examples of hope & fear in the lyrics
Small groups: kids note whether “hope” or “fear” was stronger in each example
Small groups: select two lines/stanzas that best illustrate hope or fear
Post on Padlet
Whole group: debrief; model what a “good” reflection looks like; show a skills progression
Independently: kids draft a paragraph reflection on whether they felt fear or hope was a more powerful idea in song and why, using evidence from any of the groups’ findings.
This is just one way EQ-focused lit circles or book clubs can be rigorous while meeting kids where they are. The work they do in a lesson like this does not have a right or wrong answer; the kids discuss and rehearse their ideas and thinking aloud before they put pen to paper. The EQ requires kids to think beyond plot and surface-level similarities to do this work; it pushes them to consider ideas that are bigger than a text alone.
Listen in here to get a feel for how I break down this EQ and the levels of complexity available to teachers and students with just this one question:
Believe it or not, there are even MORE reasons to lean into an EQ-centered appraoch to lit circles, and there’s a PART TWO to this blog series! Are you ready for more?