Teaching Rhetorical Analysis: Using Film Clips and Songs to Get Started with SPACE CAT
Rhetorical analysis: so much more than commercials and appeals
Rhetorical analysis can get a stuffy reputation. Sometimes, we reserve it only for “serious” classes and students and we focus on monumental, world-shaking types of speeches. While this approach accomplishes a few of our long-term goals for education, it’s not doing enough to reach the masses of students who need these skills.
I hope you’re here reading this because you want to try RA with seventh graders. You want to introduce rhetorical analysis to your struggling 10th graders. I hope you’re here because you’re trying to do RA even though you haven’t been deemed worthy and been exclusively anointed as an AP Lang teacher. I hope you’re an AP Lang teacher here looking to do things with a broader scope and new entryways into conversations about complexity and sophistication.
Really, I’m glad you’re here.
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: THE BASICS
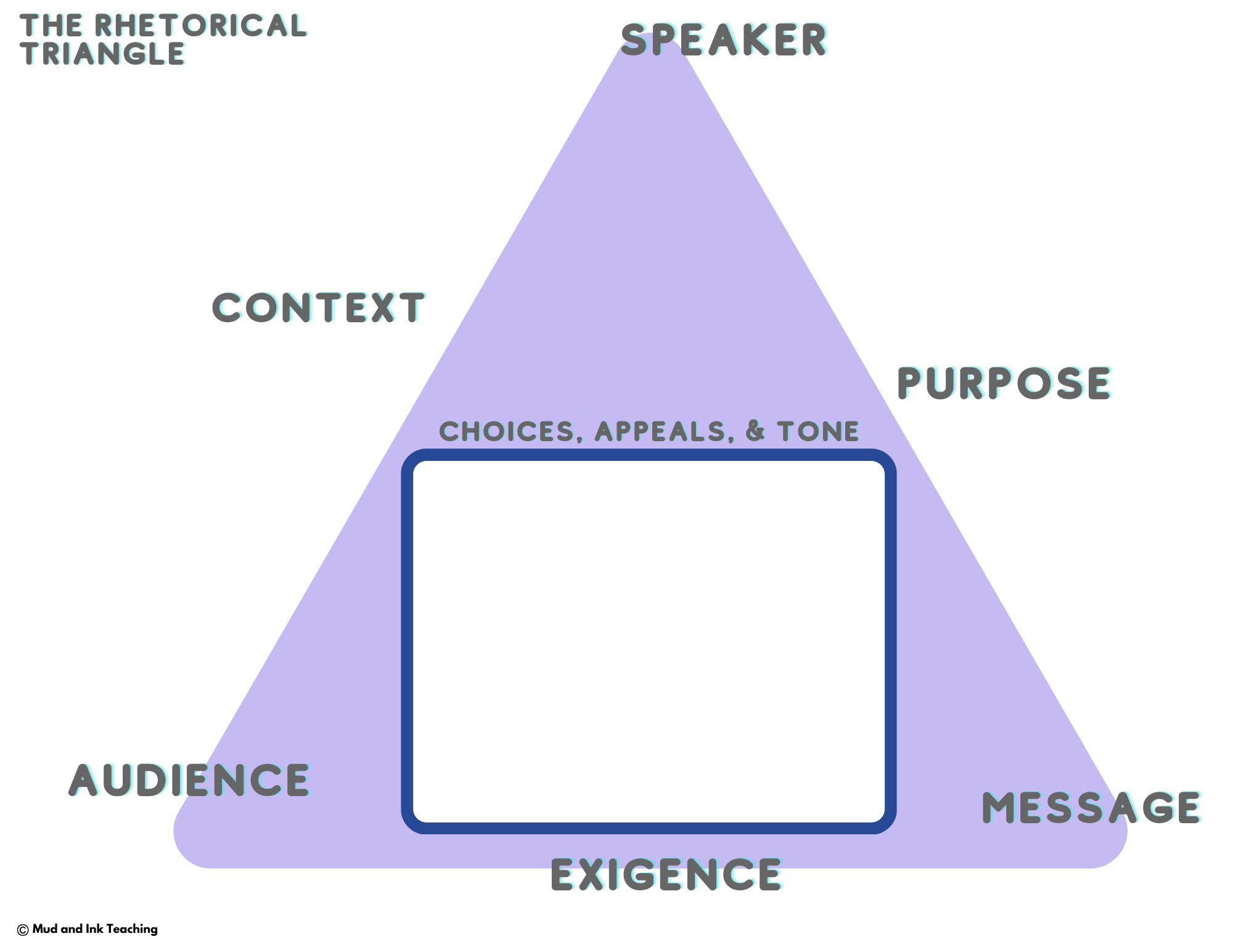
Here’s where we need to start: the triangle.
Rhetorical analysis is less about appeals and more about the unique connection between three points: the speaker, the audience, and the message.
When we start RA zeroing in on ethos, pathos, and logos, we are playing a bit of a dangerous game. Teaching terms can be a comfort zone for teachers (we do this with figurative language, too). In our field, there are so few direction instruction content types of lessons, that it can feel cozy to snuggle up with a list of terms we understand and deliver them to our students. Without realizing it, we’ve created a pretty deep hole, jumped in, and forgot to throw down the rope ladder for when we need to get back out.
When we start with terminology, we’re sending the message to students that this is the primary focus of analysis: identification. We’ve armed them with dozens of terms, so the goal of analysis must be to slap these labels all over a speech and call it annotation. Then? It ends. Students falsely believe that they’ve accomplished the task because they did exactly what you taught them. They found the rhetorical questions. They found a simile. They found an example of ethos.
And then? We get really frustrated when they can’t tell us WHY, HOW, or SO WHAT when we probe them deeper about what they’ve identified.
This is my very long way of telling you this: DON’T start with terms, or, if you do, be ready to pivot quickly!
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: WHERE TO BEGIN
START with the rhetorical triangle or a framework that you like (I like SPACE CAT) and a conversation around the rhetorical situation (SPACE). By emphasizing the importance of understanding the components of the broader context of the argument, we help students start the probing question why? in the back of their heads as we go deeper and deeper into the argument itself.
One of my favorite pieces to use for practicing the rhetorical situation is looking at Lumiere’s plea to Belle in “Be Our Guest”. In another blog post, I outline how much there is to the situation -- there is so much to consider in terms of the speaker, the purpose, the audience, the context and the exigence. In the slide deck for this lesson, we spend a great deal of time listing as many details as possible before even looking at a single lyric. Why? Because once we get into the argument, we’re seamlessly moving through true analysis.
Ms. C? I think I found a simile.
What similie is that?
Well it says ____________.
Hmm.. You’re right. So why does this particular simile hold weight knowing what we know about who Lumiere is and what he’s trying to achieve in this moment?
Wheels turning…
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: GETTING INTO THE ARGUMENT
So we’ve got a handle on the rhetorical situation. That’s a win. In fact, that might be the entire goal of a unit if you’re just beginning. If your school is taking their time and truly working on vertical articulation, this is a great skill to introduce at 9th grade and build toward mastery in 10th.
But let’s say we’re moving on a bit and ready to analyze the argument. You might have a speech, a commercial, another song, or another type of fictional scenario, and now we need to look at the techniques used and do the analysis work.
This is where we come back to our analysis framework. I like using SPACE CAT, so this stage is where I rely on CAT: choices, appeals, and tone.
Rhetorical choices include just about everything, so it’s up to you to narrow the lane of what each argument is doing well. A rhetorical choice might be the structure or organization of the argument, an extended metaphor, the use of personification, or even a particularly interesting use of parallel structure. Appeals are what you think they are: ethos, pathos, and logos. And of course, tone is exactly what you think it is, too.
Not all choices, appeals, or potential tone words are important to talk about in every speech, so fully embrace your right to decide ahead of time which choices are on the table for discussion (this is called scaffolding and if you need help with it, I have a training in my Mastering Close Reading Workshop that you might find very helpful!).
Let’s Look at an Example: “Mother knows best”
Here’s a quick example from “Mother Knows Best” in Disney’s Tangled for each of the components in CAT.
Mother Godel opens her song referring to Rapunzel “as fragile as a flower; still a little sapling, just a sprout”. She’s comparing Rapunzel to an undeveloped, extremely young plant.
She then uses the refrain “Mother Knows Best” along with other overly-assertive physical behaviors to assert her own ethos and Rapunzel’s lack of life experience.
The song also gives students the chance to look at tone, especially in the verse where Mother Godel tells Rapunzel that she won’t survive as a “sloppy, underdressed, immature, clumsy” and “gettin’ kinda chubby” girl out in the real world. This demeaning tone further underscores Mother Godel’s authority and increases the fear in Rapunzel about leaving her tower.
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: SO WHAT?
Well, we’ve arrived back where we started, friends. There’s a whole lot of highlighting, lots of phrases and details identified as one thing or another, but here comes the real work: SO WHAT?
So, Mother Godel uses a demeaning tone toward Rapunzel. So what?
She compares her to a “sapling” that has just sprouted from the ground. So what?
Here’s where we send students back to the rhetorical situation.
Support them through their “so what” with questions referring back to SPACE:
Why is this tone effective given what we know about the audience?
How does this metaphor create a sense of fear in Rapunzel?
How does Mother Godel’s use of hyperbole help her achieve her purpose?
Given the context of the situation, why would Mother Godel rely on the emotion of fear in this particular argument?
Once you’ve gotten through the SPACE, the CAT, and now arrived at the analysis part, remember that you can do this a few ways. Students oftentimes will write a paragraph of analysis, but if you’d prefer, you might have students complete a one-pager or just have a discussion that outlines what students could write about. It’s okay for some lessons to be heavier on the process than on the result.
SOME FINAL THOUGHTS…
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: TRUST THE PROCESS
This is the process. It takes time, practice, and more practice. But if you are able to confidently lean on a framework that you like, provide the right types of arguments that meet students where they’re at, and stretch their work with rhetoric over multiple years, you’re going to find increasing success.
If you’re looking for more support, I have resources that are ready to help you. Keep doing the work -- I’m right here behind you every step of the way.